← Implications And Mechanisms Of Antiviral Effects Of Lactic Acid Bacteria: A Systematic Review Red And Blue Light Induce Soybean Resistance To Soybean Mosaic Virus Infection Through The Coordination Of Salicylic Acid And Jasmonic Acid Defense Pathways →
Tau Accumulation In The Spinal Cord Contributes To Chronic Inflammatory Pain By Upregulation Of IL-1β And BDNF
Here is one of the pictures featuring the Tau Accumulation in the Spinal Cord Contributes to Chronic Inflammatory Pain by Upregulation of IL-1β and BDNF. Numerous images associated with the Tau Accumulation in the Spinal Cord Contributes to Chronic Inflammatory Pain by Upregulation of IL-1β and BDNF can be utilized as your reference point. Below, you'll find some more pictures related to the Tau Accumulation in the Spinal Cord Contributes to Chronic Inflammatory Pain by Upregulation of IL-1β and BDNF.
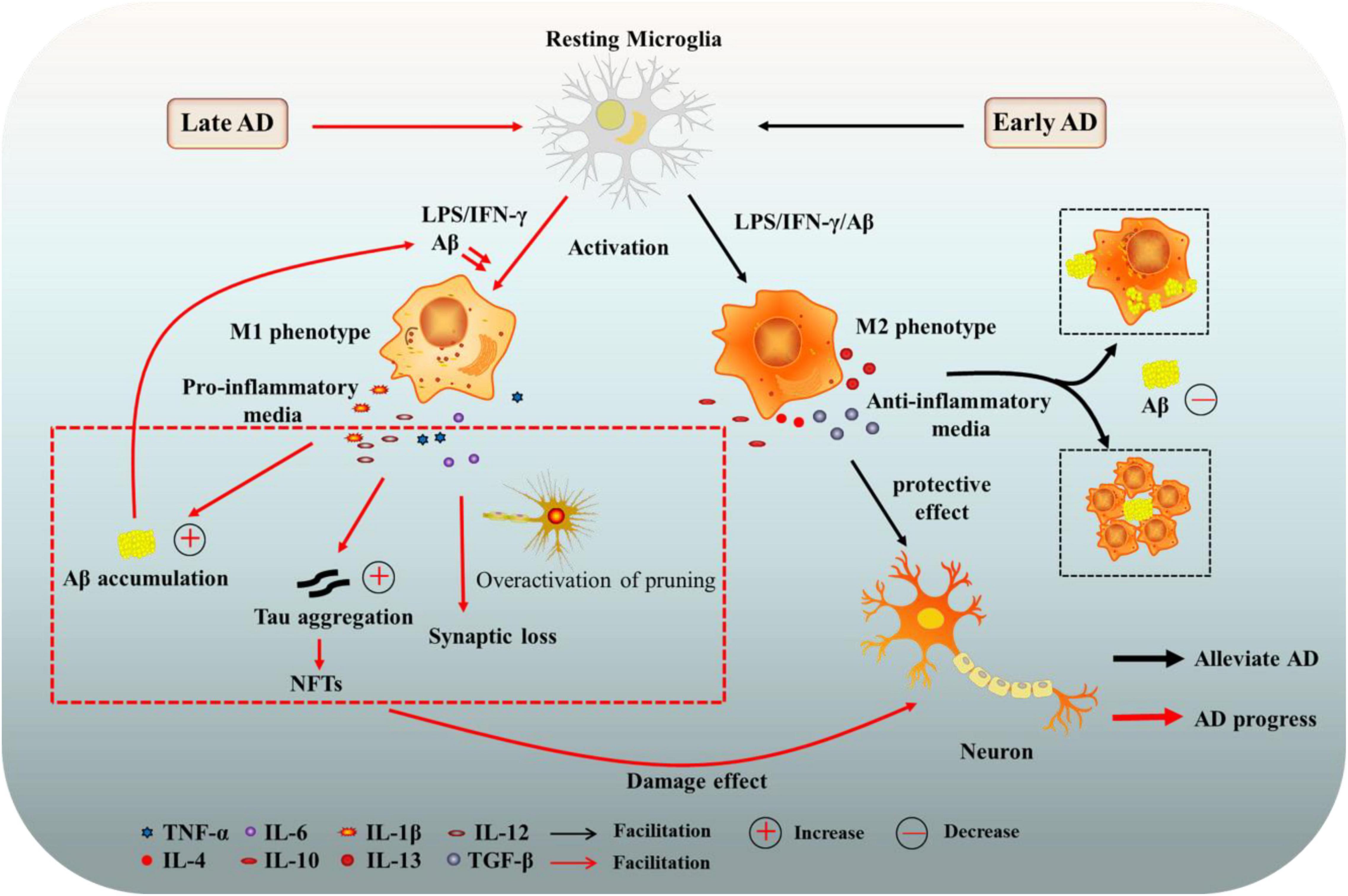 Title: Frontiers | the role of microglia in alzheimer’s disease from the
Title: Frontiers | the role of microglia in alzheimer’s disease from theFrontiers | the role of microglia in alzheimer’s disease from the.
 Title: (pdf) tau accumulation in the spinal cord contributes to chronic
Title: (pdf) tau accumulation in the spinal cord contributes to chronic(pdf) tau accumulation in the spinal cord contributes to chronic.
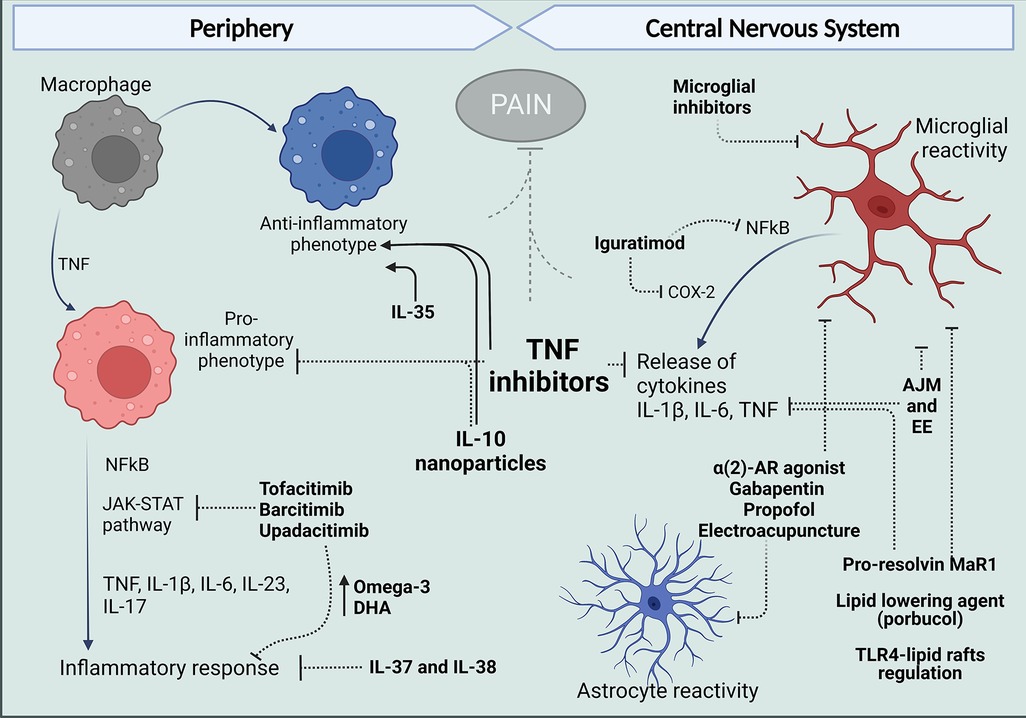 Title: Frontiers macrophages and glial cells: innate immune, 46% off
Title: Frontiers macrophages and glial cells: innate immune, 46% offFrontiers macrophages and glial cells: innate immune, 46% off.
